Reimagining Customer Experiences with ChatKit: Where AI Meets Interactive UI

Introduction: The Evolution of Customer Service AI
The retail industry is evolving its customer service interactions beyond traditional form-based processes and static interfaces. Modern customers expect intuitive, conversational experiences that understand context, intent, and provide intelligent assistance throughout their journey.
OpenAI’s ChatKit framework offers new capabilities for building sophisticated conversational AI applications. The ChatKit Order Returns Sample Application demonstrates how this technology can transform traditional customer service scenarios into dynamic, natural language-driven experiences powered by Azure OpenAI.
The ChatKit Approach: Enhanced Chat Interfaces
This application demonstrates how ChatKit transforms a traditional chat-based experience into a workflow-driven UI by combining widget-based interactions with natural language conversations. Rather than forcing every user action through LLM interpretation, ChatKit enables direct action execution via widgets, making the experience faster, more intuitive, and more reliable—while still allowing users to switch back to natural language at any point.
AI-Driven UI: The Core Innovation
The fundamental shift here is AI-driven UI—where the AI determines what interface elements to show based on conversation context. Unlike traditional applications where developers pre-define every screen and workflow, ChatKit allows the AI to dynamically generate appropriate widgets, forms, and action buttons based on what the user needs at that moment. This creates a truly adaptive experience where the UI evolves with the conversation.
The platform provides turnkey capabilities such as shimmer-like progress indicators, HTTPS/SSE streaming responses, and dynamic UI rendering, ensuring users always understand what stage of the workflow they are in and what is happening behind the scenes.
Enterprise Azure Integration: Extending OpenAI for the Cloud
Notable Implementation: This solution showcases how ChatKit, the OpenAI Agents SDK, and the Responses API have been extended for Azure OpenAI, performing real tool execution through:
- CRUD operations on Azure Cosmos DB for customer data management
- Vector search via Azure OpenAI embeddings for semantic product discovery
- Azure AI Search integration for policy and catalog lookups
- Azure AD authentication for enterprise security and compliance
The result is an enterprise-ready, transparent, and highly engaging customer experience that demonstrates the full potential of conversational AI when properly integrated with cloud-native services.
🎥 Video Demo
Click the image above to watch the demo showing the dual-interaction approach: customers speaking naturally OR clicking widgets
What Makes This Different: The ChatKit Advantage
Traditional order return systems follow a linear, form-based approach that can frustrate both customers and support teams. The ChatKit-powered solution introduces several notable capabilities:
🚀 Key Technical Improvements
| Feature | Traditional Approach | ChatKit Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Interface | Static forms with predefined fields | Dynamic widgets responding to natural language |
| User Input | Structured dropdown menus and checkboxes | Free-form conversational input |
| Process Flow | Linear, rigid step-by-step forms | Contextual, adaptive conversation flow |
| Intelligence | Rule-based validation | AI-powered intent recognition and context understanding |
| User Experience | Frustrating, impersonal | Engaging, human-like interaction |
Natural Language as the Primary Interface
A notable aspect of this application is how it elevates interaction through generative AI. Rather than requiring users to navigate complex forms or remember specific product codes, customers can describe their situation naturally:
"I want to return some items"
"I want to return Smart Home Hub from order ORD-79001"
"it was completely damaged"
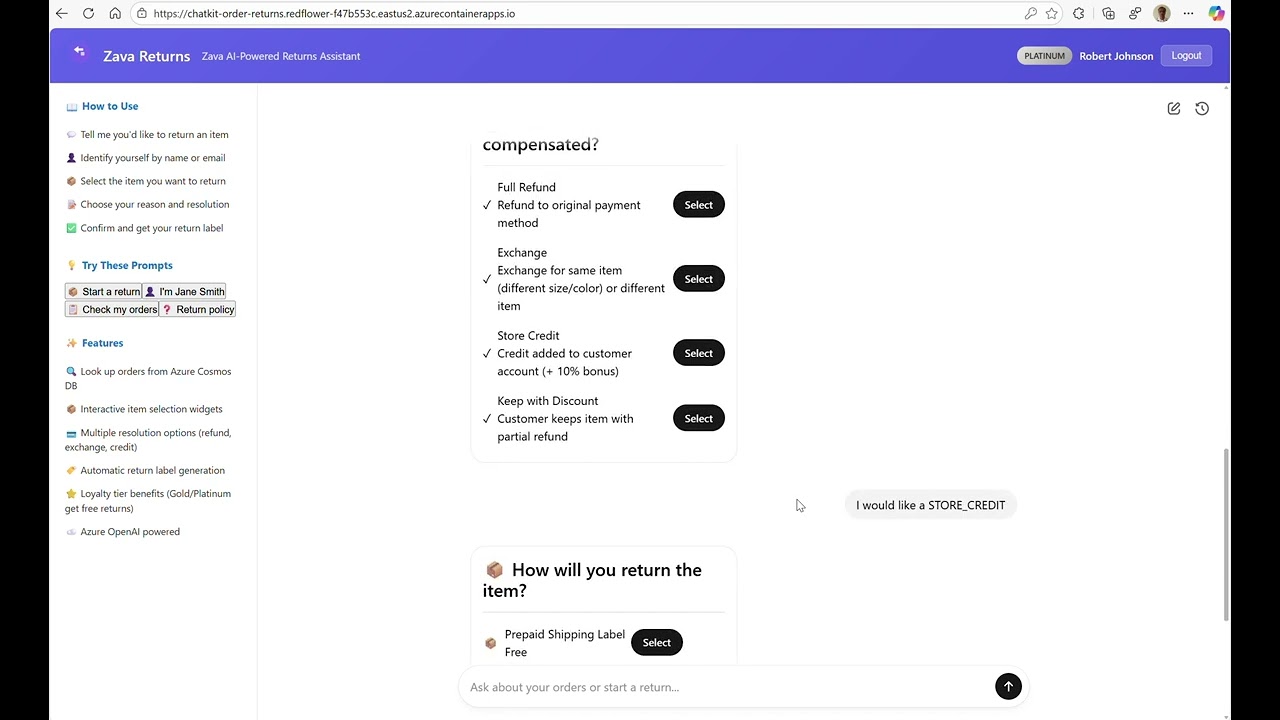
"I would like a STORE_CREDIT"
The AI understands context, extracts relevant information, and dynamically generates appropriate interface elements—all through natural language processing. Users can also choose to click widget buttons directly (like “Return This”, “Damaged/Defective”, or “Select”) instead of typing.
Architecture Deep Dive: ChatKit + Azure OpenAI + Azure Cosmos DB
The Technical Foundation
The Order Returns sample application showcases a sophisticated architecture built with modern technologies:
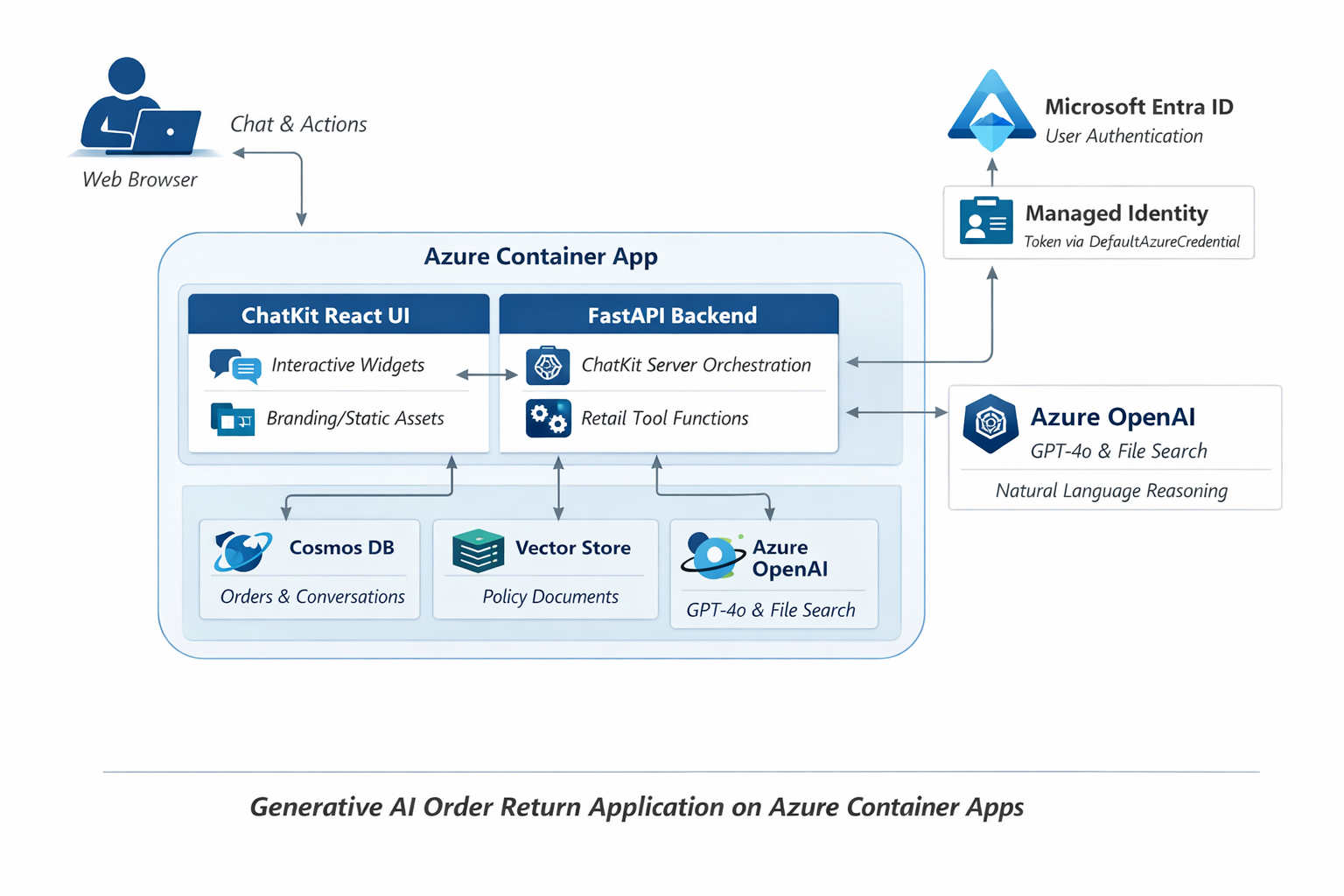
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ React Frontend │
│ (@openai/chatkit-react) │
│ Official ChatKit UI │
└─────────────────┬───────────────────────────┘
│ ChatKit Protocol (SSE)
┌─────────────────┼───────────────────────────┐
│ Python Backend │
│ FastAPI + ChatKit Server │
│ (openai-chatkit library) │
└─────────────────┬───────────────────────────┘
│
┌───────────┼────────────┐
│ │ │
┌─────▼─────┐ ┌───▼────┐ ┌─────▼─────┐
│Azure │ │ Azure │ │ Function │
│OpenAI │ │Cosmos │ │ Tools │
│GPT-4o │ │ DB │ │ │
└───────────┘ └────────┘ └───────────┘
1. ChatKit: Dual Interaction Paradigm
ChatKit enables a unique dual-mode experience where customers can either converse naturally or interact directly with UI elements. The server determines what widgets to show based on conversation context:
Python Widget Component:
# Dynamic widget generation based on conversation state
def create_return_action_widget(customer_context: Dict[str, Any]) -> Dict[str, Any]:
return {
"type": "return_actions",
"props": {
"customer_id": customer_context["id"],
"eligible_orders": customer_context["returnable_orders"],
"actions": ["quick_return", "exchange_request", "store_credit"],
"natural_language_hint": "Or tell me what you'd like to return in your own words"
}
}
React UI Component:
// Official ChatKit React integration
import { ChatKit } from '@openai/chatkit-react';
function CustomerServiceApp() {
return (
<ChatKit
endpoint="/api/chatkit"
className="h-full w-full"
placeholder="Describe what you'd like to return, or use the buttons below..."
/>
);
}
Key Feature: Customers can say “I want to return Smart Home Hub from order ORD-79001” OR click a “Return This” button—both approaches work seamlessly. domainKey={chatkitDomainKey} />
### 2. Tools Actions: Extensible Business Operations
The system uses **function calling** for business operations, but the architecture supports extension to **MCP (Model Context Protocol) Tools** for more sophisticated integrations:
#### Current Implementation: Function Tools
```python
# Variety of Azure-powered business operations
TOOLS_ACTIONS = {
# Azure Cosmos DB CRUD operations
"customer_lookup": lambda term: search_cosmos_db("customers", term),
"order_retrieval": lambda customer_id: get_customer_orders(customer_id),
"return_policy_check": lambda item_id: validate_return_eligibility(item_id),
# Azure AI Search operations
"product_search": lambda query: semantic_product_search(query),
"policy_lookup": lambda category: search_return_policies(category),
# Azure Vector Search for contextual recommendations
"similar_cases": lambda description: vector_search_similar_returns(description)
}
Future Extension: MCP Tools Support
# Architecture ready for MCP Tools integration
# MCP allows more sophisticated tool chains and external system integration
class MCPToolsAdapter:
def extend_with_mcp(self, mcp_server_url: str):
# Can extend to MCP-based tools for complex workflows
# Enterprise systems integration, multi-step approvals, etc.
pass
3. Extended ChatKit Library for Azure OpenAI
Notable Implementation: The implementation extends OpenAI’s ChatKit library to work with Azure OpenAI, enabling enterprise-grade security and compliance:
Azure OpenAI Adaptation:
# Extended ChatKit server for Azure OpenAI
from openai_chatkit import ChatKitServer
from azure.identity.aio import DefaultAzureCredential
class AzureChatKitServer(ChatKitServer):
def __init__(self):
# Override OpenAI client with Azure OpenAI client
self.client = AsyncAzureOpenAI(
azure_endpoint=os.getenv("AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT"),
azure_ad_token_provider=self._get_azure_token,
api_version="2024-06-01"
)
super().__init__(client=self.client)
async def _get_azure_token(self):
"""Enterprise authentication via Azure AD"""
credential = DefaultAzureCredential()
token = await credential.get_token(
"https://cognitiveservices.azure.com/.default"
)
return token.token
Streaming Responses with Progress:
# Real-time conversation updates with shimmer indicators
async def stream_response_with_progress(self, user_message: str):
yield {"type": "progress", "status": "thinking", "shimmer": True}
async for chunk in self.client.chat.completions.create(
model=self.deployment_name,
messages=self.conversation_history,
stream=True
):
if chunk.choices[0].delta.content:
yield {
"type": "content",
"data": chunk.choices[0].delta.content,
"shimmer": False
}
Enterprise Benefits: Azure AD authentication, data residency, compliance (SOC 2, HIPAA), custom model deployments.
Real-World Scenario Walkthrough
Let’s explore how this technology stack handles a typical return scenario:
Scenario: Returning a Damaged Item
Customer Input: “I want to return some items”
1. Intent Analysis (Agents SDK)
{
"primary_intent": "return_request",
"entities": {
"customer_id": "robert_johnson",
"order_number": "ORD-79001",
"item": "Smart Home Hub",
"reason": "damaged",
"compensation_preference": "store_credit"
},
"required_actions": [
"identify_customer",
"list_returnable_items",
"capture_return_reason",
"process_compensation"
]
}
2. Dynamic Widget Generation (ChatKit)
Based on the AI analysis, ChatKit generates contextual widgets:
const widgets = [
{
type: "CustomerProfile",
data: { name: "Robert Johnson", tier: "Platinum", email: "rjohnson@company.com" }
},
{
type: "ItemSelector",
title: "Select Item to Return",
items: [
{ name: "Ultra HD Smart Display", qty: 1, price: 299.99, daysLeft: 10 },
{ name: "Smart Home Hub", qty: 2, price: 89.99, daysLeft: 25 },
{ name: "USB-C Cable 6ft (3-Pack)", qty: 1, price: 14.99, daysLeft: 25 }
],
actions: ["Return This"]
},
{
type: "ReasonSelector",
title: "Why are you returning?",
options: ["Damaged/Defective", "Wrong Item Received", "Not As Described", "Changed My Mind", "Found Better Price", "Arrived Too Late", "Gift Return"]
},
{
type: "CompensationOptions",
title: "How would you like to be compensated?",
options: ["Full Refund", "Exchange", "Store Credit (+10% bonus)", "Keep with Discount"]
}
];
3. Contextual Conversation Flow
The application maintains context throughout the interaction:
- Customer: “I want to return Smart Home Hub from order ORD-79001”
- AI Response: “Got it — I’ve pulled up the Smart Home Hub. Why are you returning?”
- Customer: “it was completely damaged”
- AI Response: “Got it — I’ve marked the Smart Home Hub as damaged. How would you like to be compensated?”
- Customer: “I would like a STORE_CREDIT”
- Dynamic UI: Shipping options widget appears with choices like “Prepaid Shipping Label”, “Schedule Pickup”, “Customer Drop-off”, “Return to Store”
Technical Deep Dive: Real Implementation Highlights
1. Server-Driven UI with ChatKit Widgets
One of the most innovative aspects is how the Python backend creates dynamic UI widgets:
# widgets.py - Server-side widget creation
async def create_customer_widget(customer_data: Dict[str, Any]):
"""Create a customer information display widget."""
return {
"type": "customer_info",
"props": {
"customer_id": customer_data.get("id"),
"name": customer_data.get("name"),
"email": customer_data.get("email"),
"phone": customer_data.get("phone"),
"tier": customer_data.get("membership_tier", "Standard")
}
}
async def create_order_widget(order_data: Dict[str, Any]):
"""Create an order summary widget with return actions."""
returnable_items = [
item for item in order_data.get("items", [])
if item.get("returnable", False)
]
return {
"type": "order_summary",
"props": {
"order_number": order_data.get("order_number"),
"date": order_data.get("order_date"),
"total": order_data.get("total"),
"items": returnable_items,
"actions": ["return_item", "exchange_item"]
}
}
2. React Frontend: Official ChatKit Integration
The frontend uses the official @openai/chatkit-react library (v1.4.2), not custom implementations:
// App.tsx - Main application structure
import React from 'react';
import { StrictMode } from 'react';
import { createRoot } from 'react-dom/client';
import { ChatKit } from '@openai/chatkit-react';
function App() {
return (
<div className="h-screen">
<ChatKit
endpoint="/api/chatkit"
className="h-full"
/>
</div>
);
}
The package.json shows official OpenAI dependencies:
{
"dependencies": {
"@openai/chatkit-react": "1.4.2",
"react": "^18.3.1",
"react-dom": "^18.3.1"
}
}
3. FastAPI Server Integration
The main entry point shows how ChatKit integrates with FastAPI:
# main.py - Application entry point
from fastapi import FastAPI
from fastapi.middleware.cors import CORSMiddleware
from openai_chatkit.fastapi import add_chatkit_routes
app = FastAPI()
# Configure CORS for frontend communication
app.add_middleware(
CORSMiddleware,
allow_origins=["*"],
allow_credentials=True,
allow_methods=["*"],
allow_headers=["*"],
)
# Add ChatKit routes - this handles all the conversation protocol
add_chatkit_routes(app)
if __name__ == "__main__":
import uvicorn
uvicorn.run(app, host="0.0.0.0", port=8000)
class ConversationManager:
def __init__(self):
self.state = ConversationState()
self.context_window = []
def update_context(self, user_input: str, ai_response: dict):
# Maintain sliding window of conversation context
self.context_window.append({
'timestamp': datetime.now(),
'user_input': user_input,
'extracted_entities': ai_response.get('entities', {}),
'generated_widgets': ai_response.get('widgets', [])
})
# Intelligent context pruning
if len(self.context_window) > MAX_CONTEXT_SIZE:
self.context_window = self.prune_context(self.context_window)
2. Widget Intelligence System
class IntelligentWidgetSystem {
generateWidgets(conversationContext, aiResponse) {
const widgets = [];
// Analyze what information we still need
const missingInfo = this.analyzeMissingInformation(aiResponse);
// Generate appropriate input widgets
missingInfo.forEach(info => {
widgets.push(this.createContextualWidget(info, conversationContext));
});
return this.optimizeWidgetLayout(widgets);
}
createContextualWidget(infoType, context) {
switch(infoType) {
case 'product_identification':
return new ProductSearchWidget(context.userQuery);
case 'return_reason':
return new ReasonSelector(context.productType);
case 'shipping_preference':
return new ShippingOptions(context.customerTier);
}
}
}
3. Multi-Turn Conversation Handling
The system excels at maintaining context across multiple conversation turns:
def handle_multi_turn_conversation(self, current_input: str):
# Combine current input with conversation history
full_context = self.build_context_prompt(
history=self.conversation_history,
current_input=current_input,
business_context=self.retail_context
)
# Process with enhanced context understanding
response = self.azure_openai_client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4",
messages=full_context,
functions=self.available_functions,
function_call="auto"
)
return self.process_ai_response(response)
Architecture and code examples based on the production implementation: microsoft/chatkit-foundry-order-returns-sample class OrderSystemIntegration { async processReturnRequest(returnData: ReturnRequest) { // Update order status await this.orderService.updateStatus(returnData.orderId, ‘RETURN_INITIATED’);
// Generate return label
const label = await this.shippingService.generateReturnLabel(returnData);
// Trigger inventory management
await this.inventoryService.reserveReturnSlot(returnData.items);
return { success: true, trackingNumber: label.trackingNumber }; } } ```
3. Analytics and Insights
class ConversationAnalytics:
def analyze_conversation_patterns(self):
"""Extract insights from conversation data"""
patterns = {
'common_return_reasons': self.extract_return_reasons(),
'customer_satisfaction_indicators': self.analyze_sentiment(),
'process_bottlenecks': self.identify_friction_points(),
'improvement_opportunities': self.suggest_optimizations()
}
return patterns
The convergence of ChatKit, OpenAI’s Agents SDK, and Azure OpenAI creates unprecedented opportunities for businesses to reimagine their customer interactions. This isn’t just about automating existing processes—it’s about creating entirely new categories of user experience that were previously impossible.
Resources and Next Steps
Explore the Sample Application
- GitHub Repository: Chatkit-Order-Return-Sample
Related Technologies
- OpenAI ChatKit Documentation: ChatKit Docs
- Agents SDK Guide: Agents SDK Documentation
- Azure OpenAI Service: Azure OpenAI Documentation